OmniSGW Operations Guide
OmniSGW - Serving Gateway (SGW)
by Omnitouch Network Services
Table of Contents
- Overview
- Architecture
- Network Interfaces
- Key Concepts
- Getting Started
- Configuration
- Web UI - Real-Time Operations Dashboard
- Monitoring & Metrics
- Detailed Documentation
- Additional Resources
- Contributing
- Support
Overview
OmniSGW is a high-performance Serving Gateway (SGW) implementation for 3GPP LTE Evolved Packet Core (EPC) networks, developed by Omnitouch Network Services. It manages the functions for UE mobility and bearer management, including:
- Session Management - Creating, modifying, and terminating UE (User Equipment) data sessions
- Mobility Coordination - Handling handovers between eNodeBs with data forwarding
- Bearer Management - Creating and modifying dedicated bearers for different QoS requirements
- Charging Information - Tracking session events for offline charging
- User Plane Coordination - Controlling the SGW-U (User Plane) for packet forwarding
What SGW-C Does
- Accepts session requests from MME via S11 interface (GTP-C)
- Coordinates with PGW-C for PDN connectivity via S5/S8 interface (GTP-C)
- Manages bearer lifecycle including creation, modification, and deletion
- Programs forwarding rules in SGW-U via Sxa interface (PFCP)
- Handles UE mobility by managing handovers between eNodeBs
- Provides downlink data paging for suspended sessions
- Tracks charging information for offline billing systems
Architecture
Component Overview
Process Architecture
SGW-C is built on Elixir/OTP and uses a supervised process architecture:
- Application Supervisor - Top-level supervisor managing all components
- Protocol Brokers - Handle incoming/outgoing protocol messages (S11, S5/S8, Sxa)
- Session Processes - One GenServer per active UE session
- Registries - Track allocated resources (TEIDs, SEIDs, Charging IDs, etc.)
- PFCP Node Manager - Maintains PFCP associations with SGW-U peers
Each component is supervised and will automatically restart on failure, ensuring system reliability.
Real-time system health metrics can be monitored via the Web UI Application page:
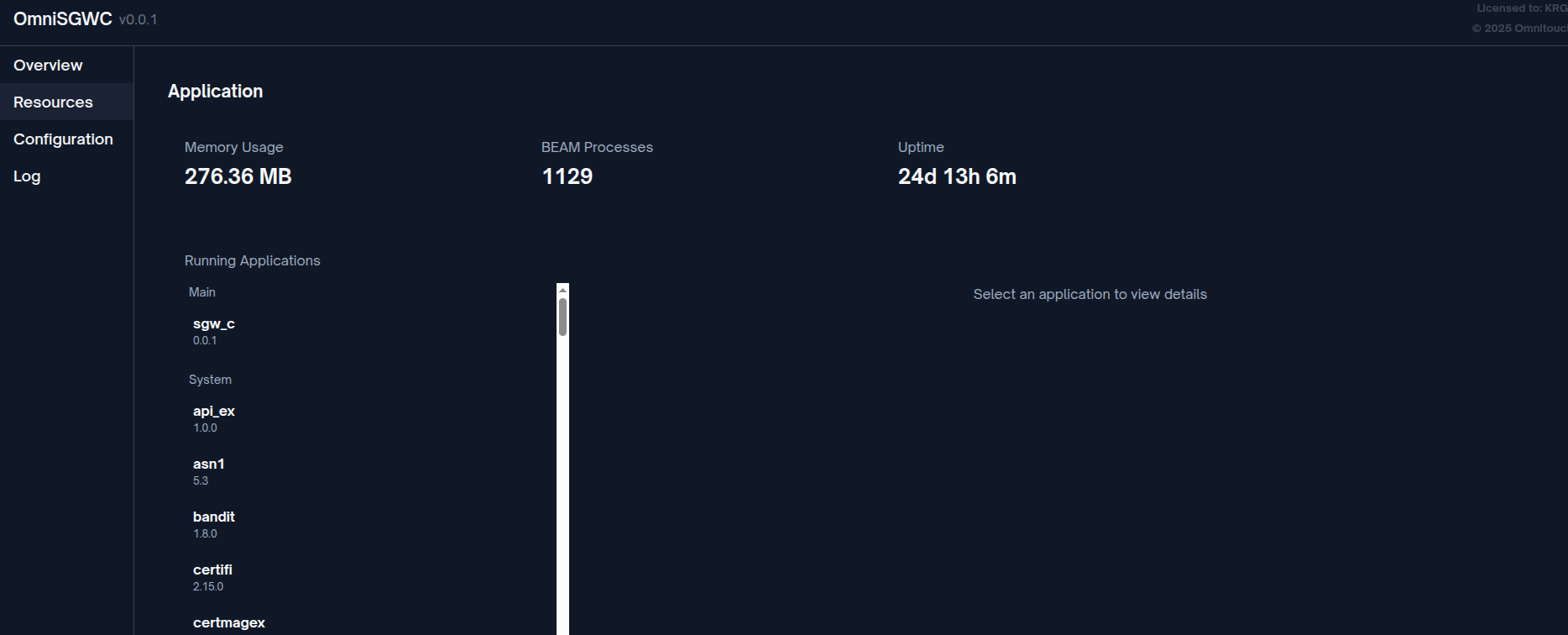
Network Interfaces
SGW-C implements three primary 3GPP interfaces:
S11 Interface (GTP-C v2)
Purpose: Control plane signaling between MME and SGW-C
Protocol: GTP-C Version 2 over UDP
Key Messages:
- Create Session Request/Response
- Delete Session Request/Response
- Modify Bearer Request/Response
- Create Bearer Request/Response
- Delete Bearer Request/Response
- Downlink Data Notification/Acknowledge
Configuration: See S11 Interface Documentation
Sxa Interface (PFCP)
Purpose: Control plane signaling between SGW-C and SGW-U
Protocol: PFCP (Packet Forwarding Control Protocol) over UDP
Key Messages:
- Association Setup Request/Response
- Session Establishment Request/Response
- Session Modification Request/Response
- Session Deletion Request/Response
- Session Report Request/Response
- Heartbeat Request/Response
Configuration: See PFCP/Sxa Interface Documentation
S5/S8 Interface (GTP-C v2)
Purpose: Control plane signaling between SGW-C and PGW-C for PDN connectivity
Protocol: GTP-C Version 2 over UDP
Key Messages:
- Create Session Request/Response
- Delete Session Request/Response
- Modify Bearer Request/Response
- Create Bearer Request/Response
- Delete Bearer Request/Response
Configuration: See S5/S8 Interface Documentation
Key Concepts
UE Session
A UE Session represents an active mobile device connected to the network. Each session manages:
- IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) - Unique subscriber identifier
- GUTI (Globally Unique Temporary Identifier) - Temporary UE identifier from MME
- MSISDN - Mobile phone number
- TAI (Tracking Area Identifier) - Current location area
- Session TEIDs - Tunnel endpoint identifiers for S11 and S5/S8
- Active Bearers - List of associated data bearers
PDN Connection
A PDN (Packet Data Network) Connection represents a UE's data connection through a specific PGW-C. Each session has:
- APN (Access Point Name) - Identifies the external network
- Charging ID - Unique identifier for billing across SGW and PGW
- TEID (Tunnel Endpoint ID) - S5/S8 interface tunnel identifier
- SEID (Session Endpoint ID) - Sxa interface session identifier
- Default Bearer - Created with every PDN connection
- Dedicated Bearers - Additional bearers for specific QoS needs
Bearer Context
A bearer represents a traffic flow with specific QoS characteristics:
- Default Bearer - Created with every PDN connection for best-effort traffic
- Dedicated Bearers - Additional bearers for specific service requirements (voice, video, etc.)
- EBI (EPS Bearer ID) - Unique identifier for each bearer within a session
- QoS Parameters - QCI (QoS Class Identifier), ARP (Allocation & Retention Priority), bitrates (MBR, GBR)
PFCP Rules
The SGW-C programs the SGW-U with packet processing rules:
- PDR (Packet Detection Rule) - Matches packets (uplink/downlink)
- FAR (Forwarding Action Rule) - Specifies forwarding behavior
- QER (QoS Enforcement Rule) - Enforces bitrate limits
- BAR (Buffering Action Rule) - Controls packet buffering during handovers
See Sxa Interface Documentation for details.
Mobility & Handover
SGW-C supports UE mobility across eNodeBs:
- Intra-MME Handover - Handover within same MME (no SGW change)
- Inter-MME Handover - Handover between MMEs with SGW relocation
- Data Forwarding - Buffering and forwarding data during handover
- Tracking Area Update - UE re-registration when moving between areas
Getting Started
Prerequisites
- Elixir ~1.16
- Erlang/OTP 26+
- Network connectivity to MME, SGW-U, and PGW-C
- Understanding of LTE EPC architecture
Verifying Operation
Check the logs for successful startup:
[info] Starting OmniSGW...
[info] Starting Metrics Exporter on 127.0.0.40:42068
[info] Starting S11 Broker on 127.0.0.10
[info] Starting S5/S8 Broker on 127.0.0.15
[info] Starting Sxa Broker on 127.0.0.20
[info] Starting PFCP Node Manager
[info] OmniSGW successfully started
Access metrics at http://127.0.0.40:42068/metrics (configured address).
Configuration
All runtime configuration is defined in config/runtime.exs. The configuration is structured into several sections:
Configuration Overview
Quick Configuration Reference
| Section | Purpose | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| metrics | Prometheus metrics exporter | Monitoring Guide |
| s11 | GTP-C interface to MME | S11 Config |
| s5s8 | GTP-C interface to PGW-C | S5/S8 Config |
| sxa | PFCP interface to SGW-U | Sxa Config |
See the Complete Configuration Guide for detailed information.
Web UI - Real-Time Operations Dashboard
OmniSGW includes a built-in Web UI for real-time monitoring and operations, providing instant visibility into system status without needing command-line tools or metrics queries.
Accessing the Web UI
http://<omnisgw-ip>:<web-port>/
Available Pages:
| Page | URL | Purpose | Refresh Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| UE Sessions | /ue_sessions | View all active UE sessions and bearers | 2 seconds |
| PFCP Sessions | /pfcp_sessions | View PFCP sessions with SGW-U | 2 seconds |
| SGW-U Status | /sgwu_status | Monitor PFCP peer associations | 2 seconds |
| Logs | /logs | Real-time log streaming | Live |
Key Features
Real-Time Updates:
- All pages auto-refresh (no manual reload needed)
- Live data streaming from OmniSGW processes
- Color-coded status indicators (green/red)
Search & Filter:
- Search sessions by IMSI, GUTI, phone number
- Instant filtering without page reload
Expandable Details:
- Click any row to see complete session details
- Inspect all active bearers and QoS parameters
- View peer configuration and capabilities
No Authentication Required (Internal Use):
- Direct access from management network
- Designed for NOC/operations team use
- Bind to management IP only for security
Operational Workflows
Session Troubleshooting:
1. User reports connectivity issue
2. Open UE Sessions page
3. Search by IMSI or phone number
4. Verify session exists and has correct:
- Tracking Area
- Active bearers and their QoS
- Tunnel endpoints established
- Correct PGW-C association
5. If no session found → Check logs for rejection reason
System Health Check:
1. Open SGW-U Status page → Verify all SGW-U peers "Associated"
2. Open UE Sessions → Check active session count vs. capacity
3. Monitor bearer distribution across APNs
Capacity Monitoring:
- Glance at UE Sessions count
- Compare to licensed/expected capacity
- Identify peak usage times
- Monitor distribution by service type
Web UI vs. Metrics
Use Web UI for:
- Individual session and bearer details
- Real-time peer status
- Quick health checks
- Troubleshooting specific users
- Verifying configuration
Use Prometheus Metrics for:
- Historical trends
- Alerting and notifications
- Capacity planning graphs
- Performance analysis
- Long-term monitoring
Best Practice: Use both together - Web UI for immediate operations, Prometheus for trends and alerts.
Monitoring & Metrics
In addition to the Web UI, OmniSGW exposes Prometheus-compatible metrics for monitoring:
Available Metrics
-
Session Metrics
teid_registry_count- Active S11/S5S8 TEIDsseid_registry_count- Active PFCP sessionscharging_id_registry_count- Active charging IDsactive_ue_sessions- Total active UE sessionsactive_bearers- Total active bearers across all sessions
-
Message Metrics
s11_inbound_messages_total- GTP-C messages received on S11s5s8_inbound_messages_total- GTP-C messages received on S5/S8sxa_inbound_messages_total- PFCP messages received- Message handling duration distributions
-
Error Metrics
s11_inbound_errors_total- S11 protocol errorss5s8_inbound_errors_total- S5/S8 protocol errorssxa_inbound_errors_total- Sxa protocol errors
Accessing Metrics
Metrics are exposed via HTTP at the configured endpoint:
curl http://127.0.0.40:42068/metrics
See Monitoring & Metrics Guide for dashboard setup and alerting.
Detailed Documentation
This section provides a comprehensive overview of all OmniSGW documentation. Documents are organized by topic and use case.
Documentation Structure
OmniSGW Documentation
├── OPERATIONS.md (This Guide)
│
└── docs/
├── Configuration & Setup
│ ├── configuration.md Complete runtime.exs reference
│
├── Network Interfaces
│ ├── sxa-interface.md Sxa/PFCP (SGW-U communication)
│ ├── s11-interface.md S11 (MME communication)
│ └── s5s8-interface.md S5/S8 (PGW-C communication)
│
└── Operations
├── session-management.md UE session lifecycle
├── bearer-management.md Bearer operations
├── cdr-format.md Offline charging records
└── monitoring.md Prometheus metrics & alerting
Documentation by Topic
🚀 Getting Started
| Document | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| OPERATIONS.md | Main operations guide (this document) | Overview and quick start |
⚙️ Configuration
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| configuration.md | Complete runtime.exs configuration reference |
🔌 Network Interfaces
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| sxa-interface.md | PFCP/Sxa interface to SGW-U |
| s11-interface.md | GTP-C S11 interface to MME |
| s5s8-interface.md | GTP-C S5/S8 interface to PGW-C |
📊 Operations & Monitoring
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| session-management.md | UE session lifecycle and operations |
| bearer-management.md | Bearer creation, modification, deletion |
| cdr-format.md | Offline charging data record format |
| monitoring.md | Prometheus metrics, Grafana dashboards, alerting |
Reading Paths
For Network Operators
- OPERATIONS.md - Overview (this document)
- configuration.md - Setup
- monitoring.md - Monitoring
- session-management.md - Day-to-day operations
For Network Engineers
- OPERATIONS.md - Architecture overview (this document)
- sxa-interface.md - User plane control
- s11-interface.md - Mobile management
- s5s8-interface.md - PDN connectivity
- session-management.md - Session lifecycle
- bearer-management.md - Bearer operations
For Configuration & Deployment
- configuration.md - Complete reference
- monitoring.md - Set up monitoring
Additional Resources
3GPP Specifications
| Spec | Title |
|---|---|
| TS 29.274 | GTP-C v2 (S11 and S5/S8 interfaces) |
| TS 29.244 | PFCP (Sxa interface) |
| TS 32.251 | Packet Switched domain charging |
| TS 32.298 | CDR encoding |
| TS 23.401 | EPC architecture |