OmniRoam
OmniRoam is Omnitouch's comprehensive wholesale revenue management solution for roaming operators. It handles the complete lifecycle of roaming data CDRs (Call Detail Records), from ingestion through rating to TAP3 file generation and reporting.
Table of Contents
Overview
OmniRoam processes roaming CDRs from mobile network operators, rates them using the OmniCharge rating engine, generates GSMA-compliant TAP3 files for billing, and provides comprehensive monitoring and reporting capabilities.
CDR Import and Rating Process
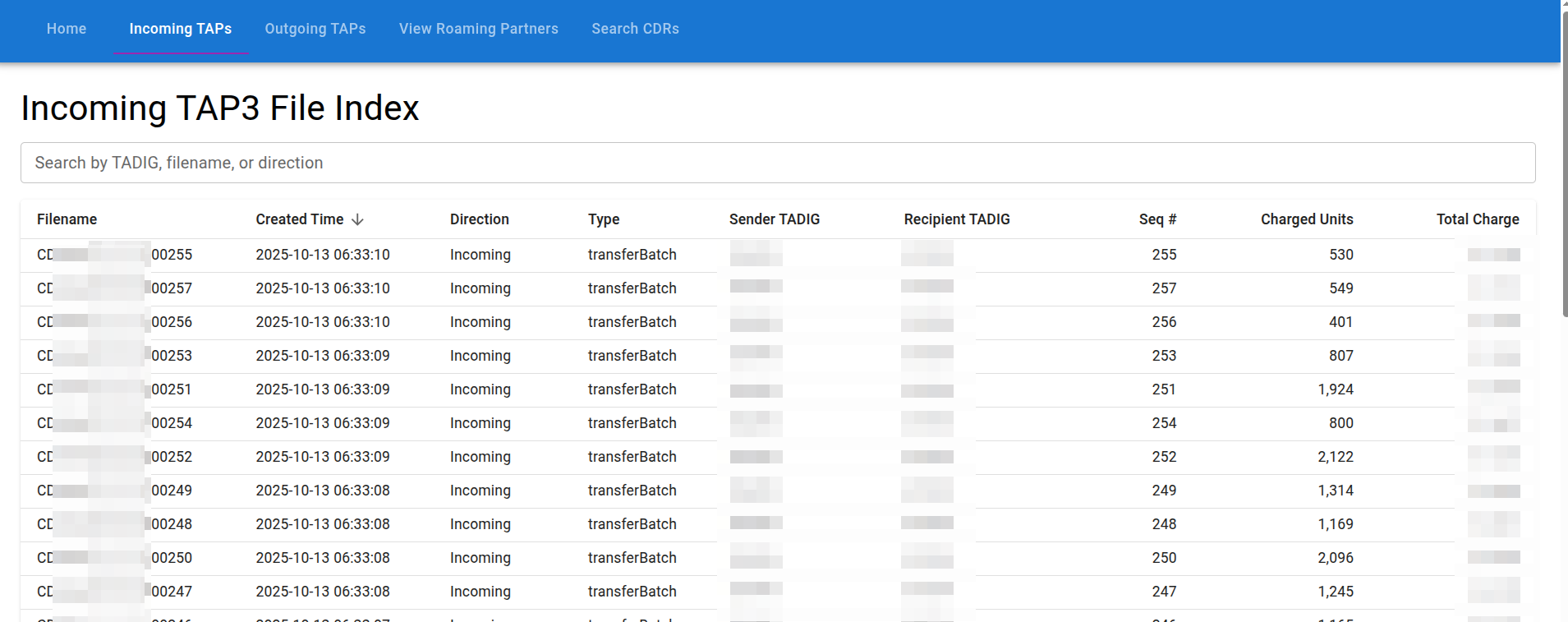
TAP3 Export Process
Operations Guide
Running TAP3 Export
# Export for specific partner
python3 export_TAP3.py VZW_Live
# Interactive mode (prompts for partner)
python3 export_TAP3.py
The export process:
- Queries CDRs from last 30 days (GSMA requirement)
- Filters out CDRs marked as already processed
- Excludes CDRs with end time less than 1 hour ago (prevents incomplete sessions)
- Groups CDRs by roaming partner
- Generates TAP3 file per partner
- Marks CDRs as processed in database
- Increments sequence counter
- Pushes metrics to InfluxDB
Monitoring & Reporting
OmniRoam pushes real-time metrics to InfluxDB for monitoring and analytics.
Metrics Collected
Raw CDR Metrics Pushed during the CDR import and rating process:
- operator: Roaming partner identifier
- input_file: Source CSV filename
- apn: Access Point Name (data service identifier)
- cellId: Cell tower identifier
- imsi: Subscriber identity
- tac: Tracking Area Code
- sGWAddress: Serving Gateway IP address
- pGWAddress: PDN Gateway IP address
- chargeableUnits: Total bytes of usage
- chargedUnits: Calculated cost
TAP Export Metrics Pushed during the TAP3 file generation process:
- operator: Roaming partner identifier
- filename: Generated TAP3 filename
- totalcharge: Total charge in TAP3 file
- totalconsumed: Total bytes in TAP3 file
- cdr_count: Number of CDRs in TAP3 file
Dashboard Queries
Example InfluxDB queries for monitoring:
Revenue by Operator
SELECT sum("totalcharge")
FROM "tap_cdr"
WHERE time > now() - 30d
GROUP BY "operator"
Data Usage by TAC
SELECT sum("chargeableUnits")
FROM "raw_cdr"
WHERE time > now() - 7d
GROUP BY "tac"
CDR Volume by Hour
SELECT count("chargeableUnits")
FROM "raw_cdr"
WHERE time > now() - 24h
GROUP BY time(1h)
Revenue by APN
SELECT sum("chargedUnits")
FROM "raw_cdr"
WHERE time > now() - 7d
GROUP BY "apn"
Grafana Integration
Create Grafana dashboards using these metrics for:
- Real-time revenue monitoring
- Traffic pattern analysis
- Partner performance tracking
- Network resource utilization
- Anomaly detection
- Billing reconciliation
Troubleshooting
CDR Import Issues
Check logs at /tmp/import_CDR_Logger_Marben_*.log
Common issues:
- Invalid IMSI format
- Missing required fields
- Timezone conversion errors
- Duplicate charging IDs
TAP3 Export Issues
Check logs at /tmp/tap3_export_*.log
Common issues:
- No CDRs in last 30 days
- Missing TAC configuration
- Invalid sequence number
- Database connection errors
OmniCharge Rating Errors
Review OmniCharge logs for:
- Missing rate plans
- Account not found
- Invalid usage values
- Currency conversion errors
InfluxDB Connection Issues
Verify:
- InfluxDB URL reachable
- Valid authentication token
- Bucket exists
- Network connectivity
Support & Maintenance
Log Locations
- CDR Import:
/tmp/import_CDR_Logger_Marben_*.log - TAP Export:
/tmp/tap3_export_*.log
Key Configuration Files
- config.yaml - Main configuration (partner rates, network settings, InfluxDB connection)
- counters.yaml - TAP3 file sequence counters
Regular Maintenance Tasks
- Monitor sequence counters - Ensure they don't exceed 99999
- Archive old TAP files - Move files older than retention period
- Monitor InfluxDB disk usage - Configure retention policies
- Review rate configurations - Update when partner rates change
- Backup configuration files - config.yaml and counters.yaml
- Monitor CDR backlog - Ensure timely processing
System Architecture
High-Level Architecture
CDR Import Process
OmniRoam uses a two-stage import process with Cache as a temporary aggregation layer for assembling partial CDR records into complete, billable CDRs.
Understanding Partial CDRs
Mobile network elements (S-GW/P-GW) don't generate a single CDR for a data session. Instead, they produce multiple partial CDR records throughout the session lifecycle:
- Start Record: Generated when the data session begins
- Update Records: Generated periodically during the session (e.g., every 15 minutes or every 100 MB of data usage)
- Stop Record: Generated when the session ends
Each partial record contains incremental usage data. For accurate billing, OmniRoam must:
- Identify which partial records belong to the same data session
- Aggregate the usage data from all partial records
- Calculate the total session duration
- Assemble one complete CDR representing the entire session
Why Cache for CDR Aggregation?
Cache serves as a high-performance temporary holding area where partial CDRs accumulate until the session is complete. Cache provides:
- Fast key-value lookups - Instantly find existing partial CDRs for a session
- In-memory storage - High-speed read/write operations for real-time aggregation
- Atomic operations - Safe concurrent updates from multiple import processes
- Persistence - CDRs survive system restarts during the aggregation window
Two-Stage Import Architecture
Stage 1: CSV Parsing and Partial CDR Aggregation
The first stage continuously reads CSV files from S-GW network elements and aggregates partial CDRs in Cache.
How Partial CDRs Are Identified and Matched
OmniRoam must determine which partial records belong to the same data session. Each session is uniquely identified by a composite Session ID consisting of:
- Charging ID: Unique session identifier from the network element
- IMSI: Subscriber identity (mobile number identifier)
- Date: Session date in the serving network's timezone
- P-GW IP Address: Gateway that handled the session
- TAC: Tracking Area Code (cell tower location)
- QCI: Quality of Service class
This combination ensures that all partial records from the same data session are grouped together, even when multiple files arrive out of order.
How Partial CDRs Are Aggregated
When the CSV parser processes each partial CDR:
- Generate Session ID from the CDR fields
- Check Cache to see if this session already exists
- If session exists in Cache:
- Retrieve the accumulated CDR data
- Verify this file hasn't been processed before (prevents duplicates)
- Add the new usage data: incoming bytes + outgoing bytes
- Update the session duration using the earliest and latest timestamps
- Store metadata about this partial record for audit purposes
- Save the updated CDR back to Cache
- If new session:
- Create a new CDR entry in Cache
- Initialize usage counters and session metadata
- Record the first partial record's timestamp
Audit Trail and Metadata
Every partial record that contributes to a CDR is tracked with comprehensive metadata:
- Source filename: Which CSV file contained this partial record
- Timestamp: When the network element generated this record
- Processing time: When OmniRoam received and processed it
- Usage contribution: How much data this partial added (incoming/outgoing bytes)
- Event type: Whether this was a start, update, or stop record
- Serving network timezone: For accurate timestamp conversion
Why metadata is critical for accounting:
This audit trail allows OmniRoam to trace a single charge end-to-end through every processing stage, which is essential for:
- Dispute resolution: When partners challenge a charge, operators can show exactly which source files contributed to it
- Revenue reconciliation: Verify that all billable usage was captured and nothing was missed or duplicated
- Regulatory compliance: Demonstrate proper handling of billing records for auditing purposes
- Debugging: Quickly identify issues in the CDR aggregation process by tracing the complete data flow
- Financial accuracy: Ensure every dollar charged can be traced back to specific network events
Session Duration Calculation
The total session duration is calculated by finding:
- Earliest timestamp across all partial records (session start)
- Latest timestamp across all partial records (session end)
- Duration = Latest - Earliest
For sessions where only update records exist (missing start/stop), the duration defaults to 24 hours.
Stage 2: CDR Assembly and Rating
The second stage periodically scans Cache for completed sessions, assembles the final CDRs, and submits them to OmniCharge for rating.
How Complete CDRs Are Selected from Cache
The CDR Assembly Process runs continuously and examines all sessions stored in Cache:
- Scan Cache for all accumulated CDR sessions
- Process in batches of 1,000 sessions at a time
- For each session:
- Extract the session date from the Session ID
- Skip if too old (> 30 days): Delete from Cache (prevents stale data buildup)
- Skip if too recent (< 24 hours): Leave in Cache for more partial records to arrive
- Load the complete CDR with all accumulated data
The 24-Hour Waiting Period
Why does OmniRoam wait 24 hours before rating a CDR?
- Partial records arrive out of order: Network congestion can delay CSV file delivery by hours
- Sessions span midnight: A session starting at 11:50 PM generates files on two different dates. The same charging ID can span multiple days, with partial records dated differently
- Update records are delayed: Periodic update records may arrive well after the session ends
- Asynchronous file generation: Different network elements export files on different schedules
- Long-running sessions: Data sessions can last hours or days, with update records trickling in throughout
By waiting 24 hours, OmniRoam ensures all partial records have arrived and the CDR is truly complete before billing.
CDR Validation and Enrichment
Before rating, each assembled CDR goes through validation and enrichment:
-
Validate completeness:
- Check if start/stop records are present
- If only update records exist, set duration to 24 hours (default)
-
Discard invalid CDRs:
- Zero usage sessions are deleted (no billable activity)
-
Calculate final usage:
- Sum all incoming and outgoing bytes
- Apply partner-specific rounding rules (e.g., round up to nearest 1 KB)
-
Enrich with location data:
- Map TAC (Tracking Area Code) to serving network location
- Add timezone information for accurate timestamps
- Add geographic location description
-
Submit to OmniCharge:
- Send the complete, enriched CDR for rating
- Receive back the calculated charge
-
Store and clean up:
- Save the rated CDR to Database database
- Push metrics to InfluxDB for reporting
- Delete the processed CDR from Cache
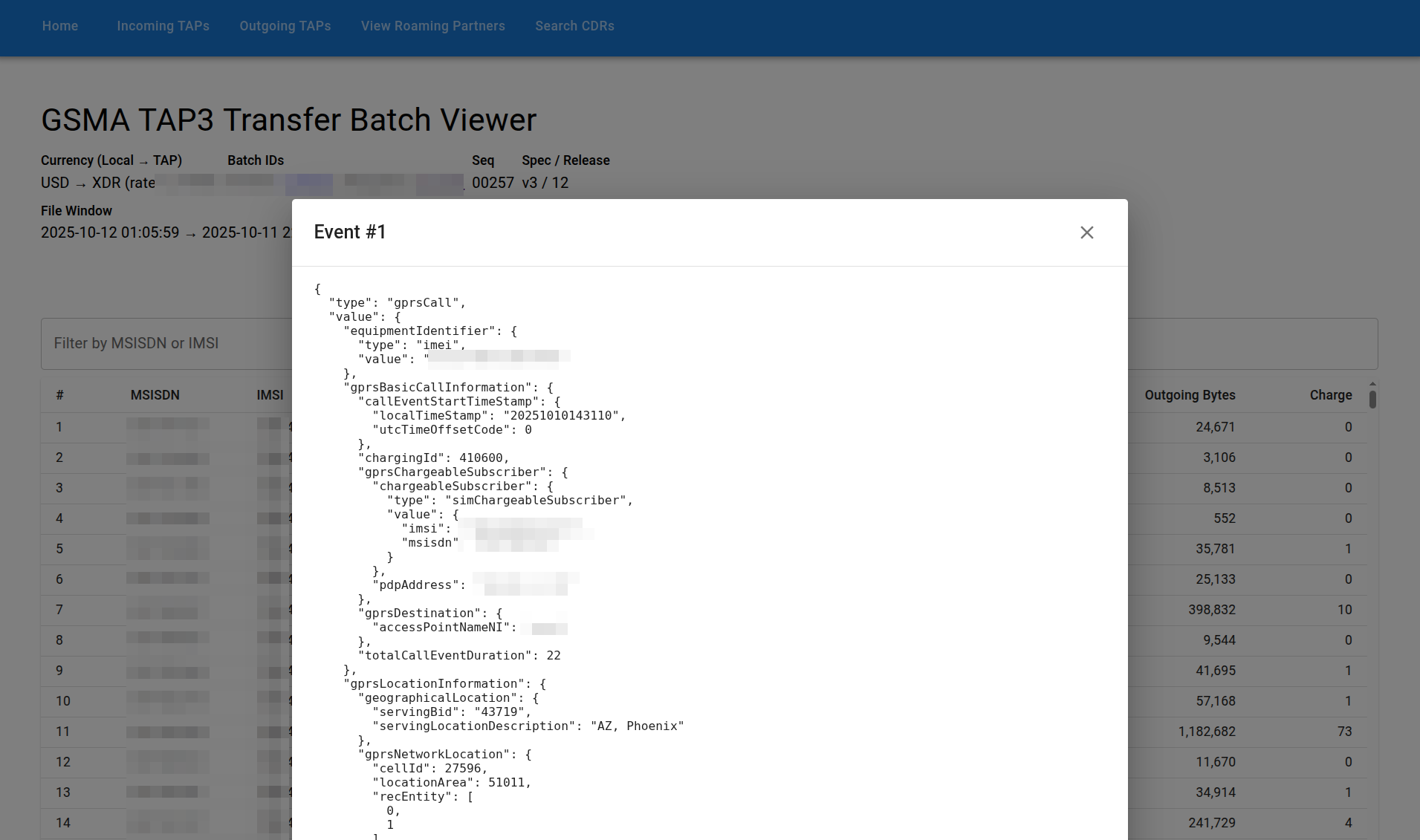
CDR Data Structure
Each aggregated CDR contains:
- Subscriber Information: IMSI, MSISDN, IMEI
- Network Information: Serving Gateway (S-GW), PDN Gateway (P-GW), Cell ID, TAC (Tracking Area Code)
- Session Details: Start/End timestamps, Duration, APN (Access Point Name)
- Usage Data: Data Volume Incoming/Outgoing, Total Chargeable Units
- Location Information: Serving BID (Network ID), Geographic Location
- QoS Information: QCI (QoS Class Identifier)
Data Processing Rules
Usage Rounding
CDRs are rounded based on partner-specific configuration in config.yaml:
partners:
Example_Live:
round_up_to: 1024 # Round usage to nearest 1KB
The system:
- Calculates total usage:
dataVolumeIncoming + dataVolumeOutgoing - Rounds up to the configured unit (e.g., 1024 bytes)
- Preserves original values for auditing
TAC-Based Localization
The system determines serving network location based on TAC (Tracking Area Code):
config:
tac_config:
Global:
tac_list: ['1101', '10000', '10100']
servingBid: 72473
servingLocationDescription: 'Smallville USA'
timezone: 'America/Smallville'
This enables:
- Proper timezone conversion for timestamps
- Geographic location assignment
- Serving network identification
OmniCharge Rating Engine
OmniRoam sends CDRs to OmniCharge, the powerful rating engine that calculates charges based on configurable rate plans.
Rating Process
Rate Configuration
Rates are configured per roaming partner in the configuration file:
partners:
Example_Live:
imsi_prefixes:
- 99901
rates:
unit_price: 0.000476800 # Price per unit
unit_bytes: 1024 # Unit size in bytes
batch_info:
sender: AUSIE
recipient: AAA00
accountingInfo:
localCurrency: 'USD'
tapCurrency: 'USD'
roundingAction: 'Simple'
tapDecimalPlaces: 5
IMSI Prefix Matching
OmniRoam matches CDRs to roaming partners using IMSI prefix matching with longest-match-first logic. This allows operators to create specific configurations for test SIMs while maintaining general configurations for production traffic.
How Prefix Matching Works
When rating a CDR, OmniRoam:
- Extracts the IMSI from the CDR (e.g.,
310410123456789) - Evaluates all partner configurations in order
- Finds the longest matching prefix
- Applies that partner's rates and configuration
Example: Test SIM Configuration
This feature is particularly useful for TADIG/IREG testing where test SIMs need different handling:
partners:
Demo_Test:
imsi_prefixes:
- 0010112345123 # Test SIM range (9-digit prefix)
rates:
unit_price: 0.0 # No charge for test traffic
batch_info:
sender: AUSIE
recipient: AAA00TEST
Demo_Production:
imsi_prefixes:
- 001011 # Production range (6-digit prefix)
rates:
unit_price: 0.000476800
batch_info:
sender: AUSIE
recipient: AAA00
Matching behavior:
- IMSI
00101123451234→ MatchesDemo_Test(9-digit prefix is longer) - IMSI
00101023456789→ MatchesDemo_Production(6-digit prefix)
This ensures test traffic goes to test TAP files with test TADIG codes, while production traffic is billed normally with production TADIG codes.
Rating Calculation
For each CDR:
- Match Partner: Identify roaming partner by IMSI prefix
- Calculate Units:
totalBytes / unit_bytes - Apply Rate:
units × unit_price = charge - Apply Rounding: Round based on
roundingAction(Up/Down/Simple) - Convert to TAP Units: Multiply by 1000 for TAP3 format
Example:
Usage: 52,428,800 bytes (50 MB)
Unit Size: 1024 bytes
Units: 51,200
Rate: $0.000476800 per 1KB
Charge: 51,200 × $0.000476800 = $24.41
TAP Units: 24,410 (24.41 × 1000)
QCI-Based Call Type Assignment
Quality of Service Classes (QCI) are mapped to TAP3 Call Type Levels:
call_type_level:
qci_1: 20 # Conversational (Voice)
qci_2: 22 # Conversational (Video)
qci_3: 23 # Real-time Gaming
qci_4: 24 # Buffered Streaming
qci_5: 20 # IMS Signaling
qci_6: 26 # Interactive (Browsing)
qci_7: 27 # Interactive (Gaming)
qci_8: 28 # Background
qci_9: 29 # Background (Low Priority)
default: 20
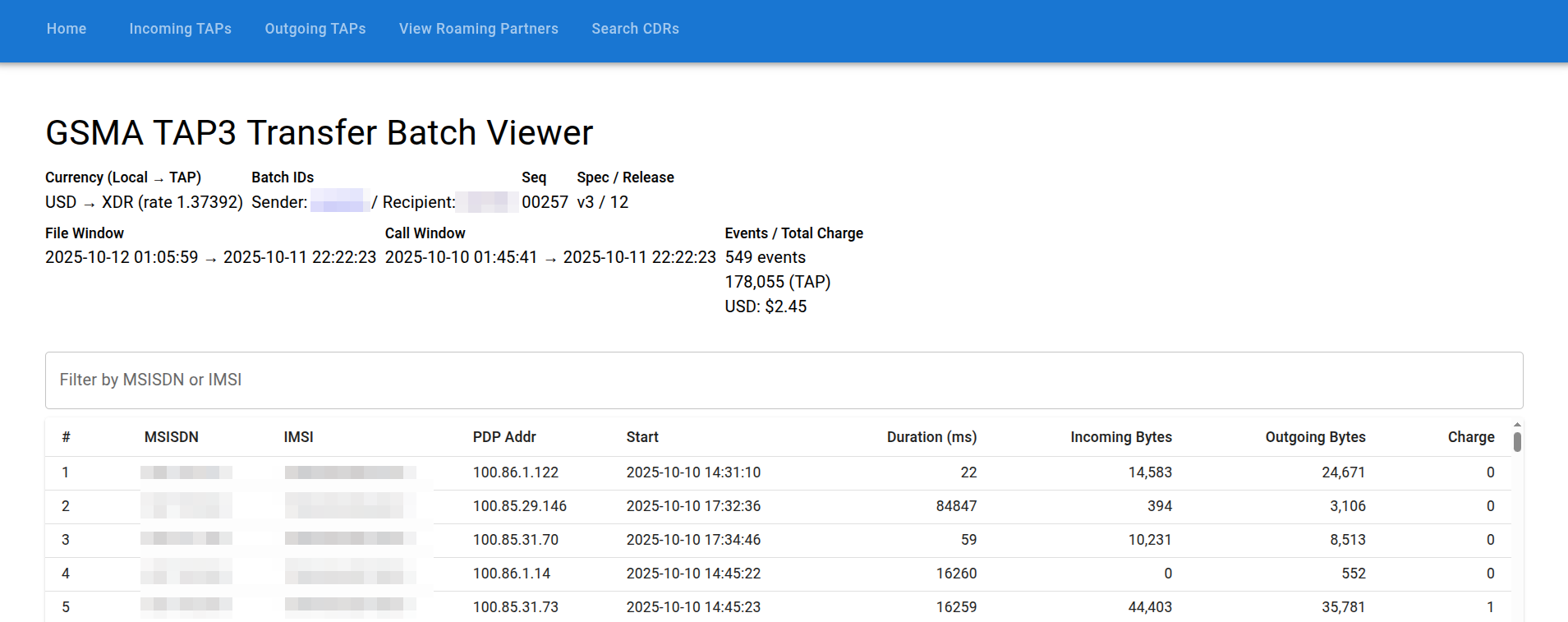
TAP3 File Generation
After CDRs are rated by OmniCharge, OmniRoam generates GSMA-standard TAP3 files for wholesale billing.
TAP3 Export Flow
TAP3 File Structure
File Naming Convention
TAP3 files follow GSMA naming standards:
<FileType><Sender><Recipient><SequenceNumber>
Examples:
CDAUSIEAAA0000001 - Commercial Data file from AUSIE to AAA00, sequence 1
TDAUSIEAAA0000001 - Test Data file from AUSIE to AAA00, sequence 1
Where:
- FileType:
CD(Commercial) orTD(Test) - Sender: 5-character TADIG code
- Recipient: 5-character TADIG code
- SequenceNumber: 5-digit sequence (from counters.yaml)
Configuration Guide
Partner Configuration
Add roaming partners in config.yaml:
partners:
ONS_Live:
imsi_prefixes: # List of IMSI prefixes for this partner
- 505057
accessPointNameOI: mnc057.mcc505.gprs
rates:
unit_price: 0.000476800 # Price per unit in dollars
unit_bytes: 1024 # Number of bytes per unit
batch_info:
sender: AUSIE # Your TADIG code
recipient: AAA00 # Partner TADIG code
specificationVersionNumber: 3
releaseVersionNumber: 12
accountingInfo:
localCurrency: 'USD'
tapCurrency: 'USD'
roundingAction: 'Simple' # Up/Down/Simple
tapDecimalPlaces: 5
round_up_to: 1024 # Round usage to nearest N bytes
call_type_level: # QCI to Call Type Level mapping
qci_1: 20
qci_2: 22
default: 20
Sequence Counter Configuration
Initialize sequence counters in counters.yaml:
AAA00:
CD: 1 # Commercial Data sequence
TD: 1 # Test Data sequence
AAA01:
CD: 1
TD: 1
Sequences auto-increment with each TAP file generated.
Network Configuration
Configure TAC-to-location mappings:
config:
tac_config:
LocationName:
tac_list: ['1101', '10000']
servingBid: 72473
servingLocationDescription: 'Network Location'
timezone: 'America/New_York'
InfluxDB Configuration
Configure InfluxDB connection in config.yaml:
config:
influx_db:
influxDbUrl: 'http://10.3.0.135:8086'
influxDbOrg: 'omnitouch'
influxDbBucket: 'Omnicharge_TAP3'
influxDbToken: 'your-token-here'
Output Paths
Configure file output locations:
config:
tap_output_path: '/etc/pytap3/OutputFiles'
tap_human_readable_output_path: '/etc/pytap3/OutputFiles_Human'
tap_in_path: '/home/user/TAP_In/'
Architecture Decisions
Why OmniCharge?
OmniCharge provides:
- Powerful rating engine with flexible rate plans
- Real-time rating capabilities
- CDR deduplication
- Comprehensive audit trails
- API-based integration
Why InfluxDB?
Advantages:
- Time-series optimized for CDR metrics
- High write throughput
- Efficient storage with compression
- Built-in downsampling
- Native Grafana integration
Workflow Summary
OmniRoam - Professional roaming revenue management by Omnitouch.