OmniCRM API
All functions within OmniCRM are accessible via the API - There is no functionality that is only available in the UI.
This allows you to integrate OmniCRM with other systems or automate tasks.
The API is a RESTful API, and is secured using multiple authentication methods including JWT tokens, API keys, and IP whitelisting.
The API is documented using Swagger, a tool that allows easy reading, understanding, and testing of API functionality.
The API documentation is available at the following URL:
Authentication Methods
OmniCRM supports three authentication methods, each designed for different use cases:
- JWT Bearer Tokens - For interactive user sessions (Web UI, mobile apps)
- API Keys - For server-to-server integrations and automation scripts
- IP Whitelisting - For trusted internal systems (provisioning servers, monitoring tools)
JWT Bearer Token Authentication
This is the primary authentication method for user sessions. Users log in with email and password, receive a JWT token, and use it for subsequent requests.
Use Cases:
- Web UI authentication
- Mobile app authentication
- Short-lived programmatic access
How to Authenticate:
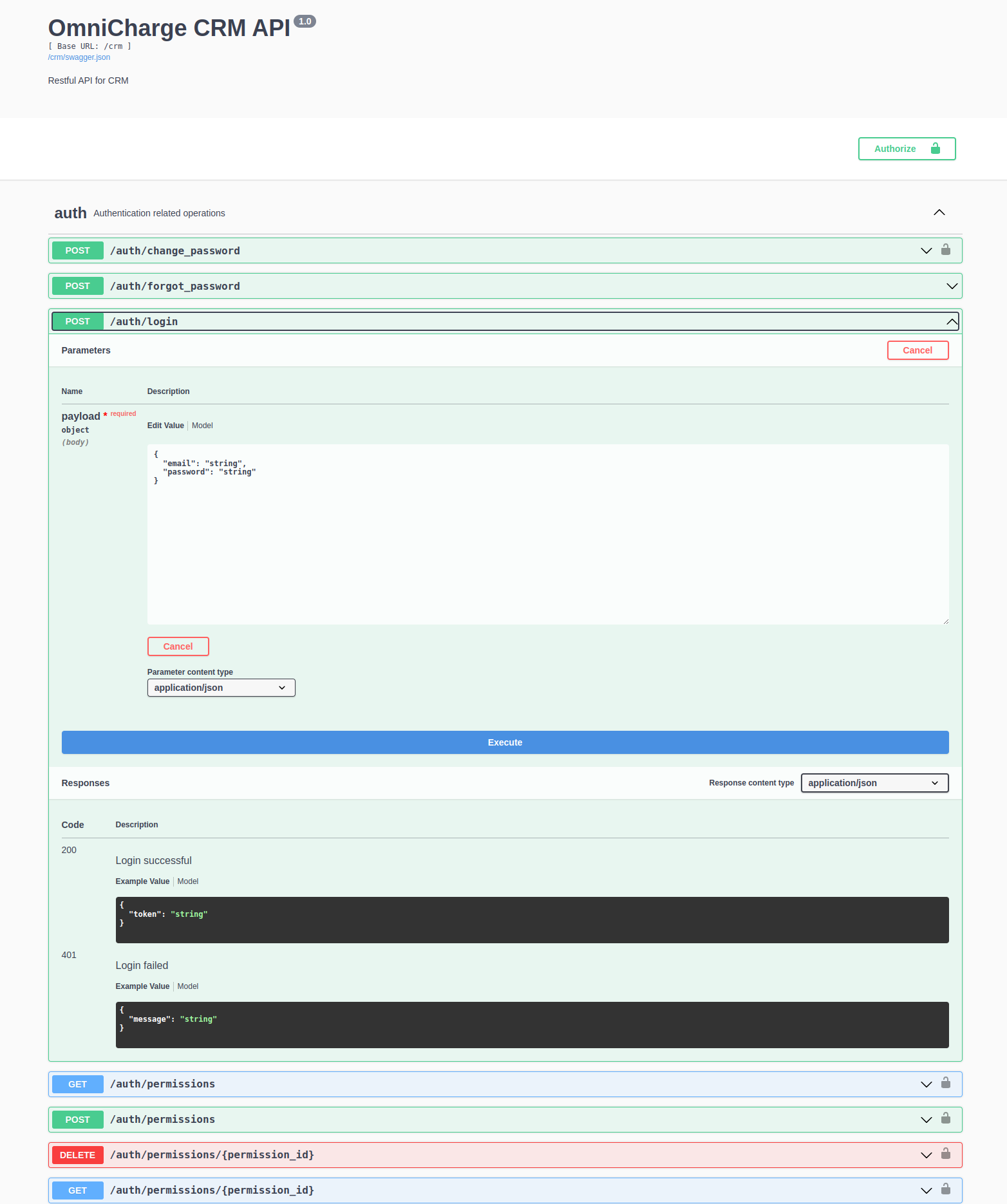
To log in, send a JSON body with the following structure to
/crm/auth/login as a POST request:
{
"email": "youruser@yourdomain.com",
"password": "yourpassword"
}
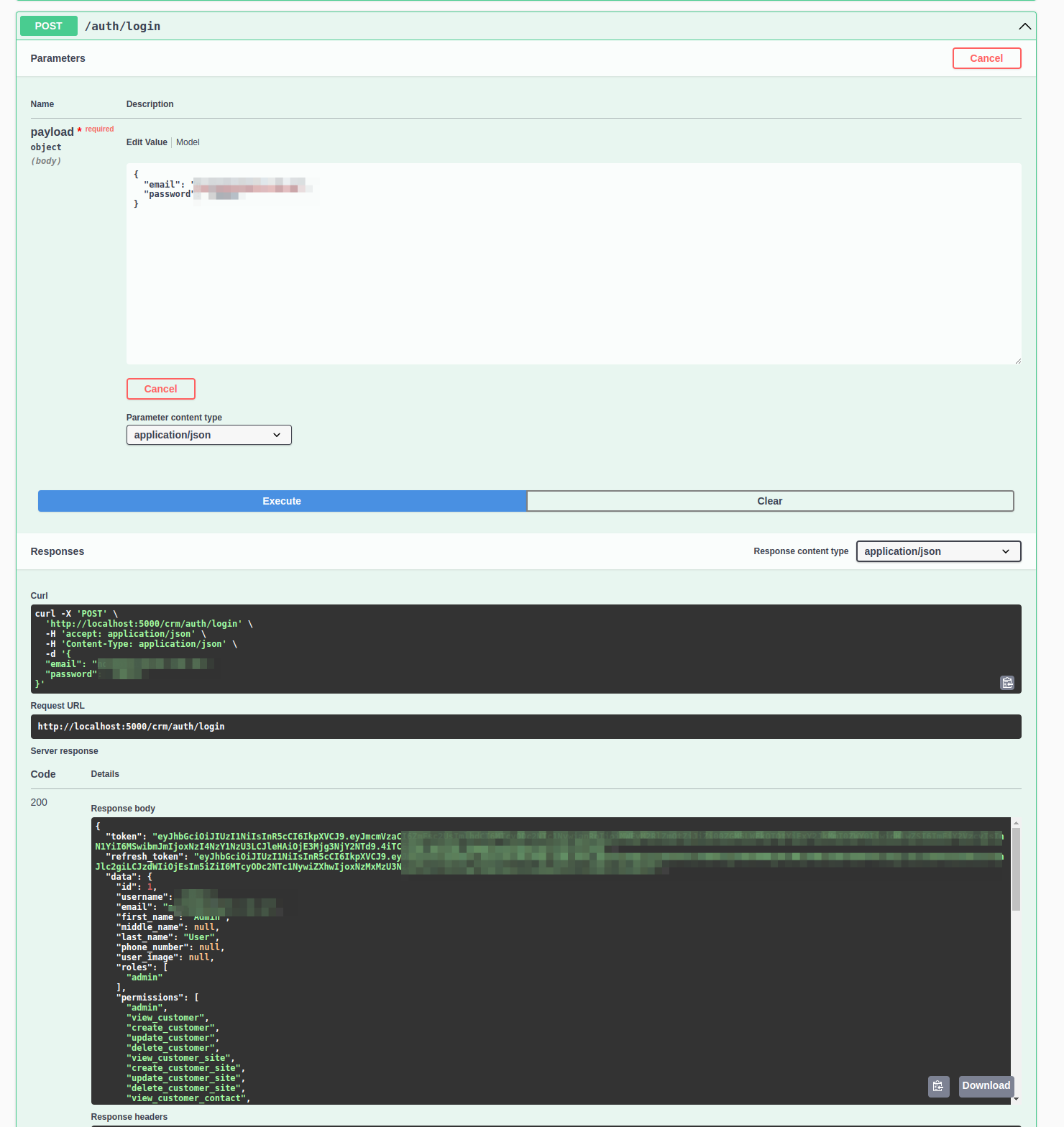
The API will return a JSON object containing a token field, which is
used to authenticate all future requests. Additionally, the response
includes a refresh_token that can be used to refresh the token when it
expires, along with the user's permissions and roles.
You can test this from the Swagger page by selecting the /auth/login
endpoint, filling in your Username and Password, and clicking the
Try it out button.
To authorize the session, copy the token value and click the
"Authorize" button at the top-right of the Swagger page. Paste the
token into the "Value" field, prefixed by Bearer and click
"Authorize".
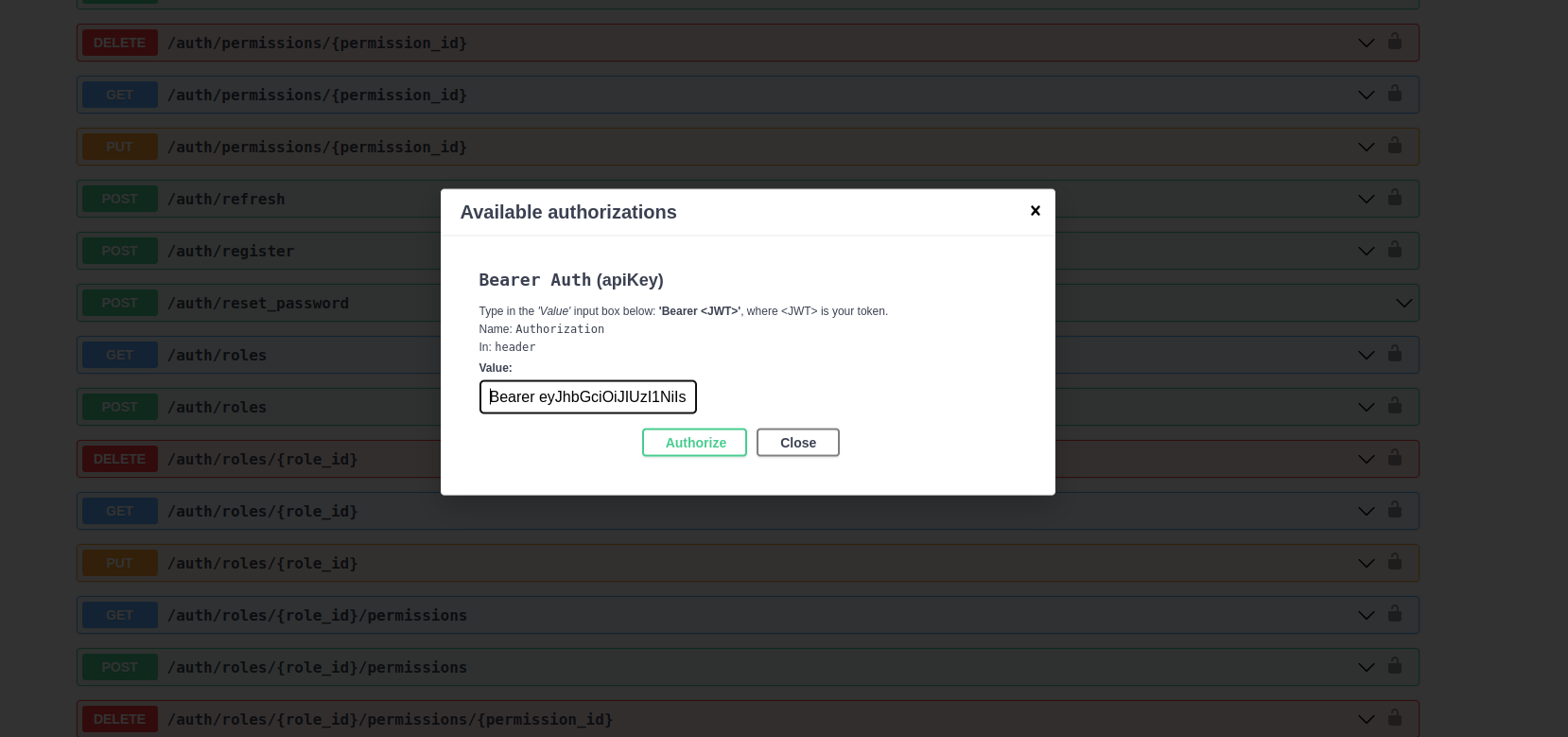
Now, all subsequent requests will be authenticated with this token.
API Key Authentication
API keys provide secure, long-lived authentication for server-to-server integrations and automation scripts without requiring user passwords.
Use Cases:
- Automated provisioning systems
- Monitoring and alerting tools
- Integration with external systems
- Scheduled tasks and cron jobs
How API Keys Work:
API keys are configured in the crm_config.yaml file and are associated
with specific roles and permissions. Each API key is a secure random
string (minimum 32 characters) that authenticates requests when passed
in the X-API-KEY header.
Configuring API Keys:
API keys must be added to crm_config.yaml by an administrator with
server access:
api_keys:
your-secure-api-key-here-minimum-32-chars:
roles:
- admin
description: "Provisioning automation system"
another-api-key-for-monitoring-system:
roles:
- view_customer
- view_service
description: "Monitoring and alerting"
Using API Keys:
Include the API key in the X-API-KEY header of your requests:
curl -X GET "https://yourcrm.com/crm/customers" \
-H "X-API-KEY: your-secure-api-key-here-minimum-32-chars"
Python Example:
import requests
crm_url = 'https://yourcrm.com'
api_key = 'your-secure-api-key-here-minimum-32-chars'
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-API-KEY": api_key
}
# Get Customers
response = requests.get(crm_url + '/crm/customers', headers=headers)
for customer in response.json()['data']:
print(customer)
Best Practices:
- Generate API keys using cryptographically secure random generators
(
openssl rand -base64 48) - Use different API keys for different systems
- Document the purpose of each API key in the
descriptionfield - Rotate API keys periodically
- Never commit API keys to version control
- Assign minimal necessary permissions to each API key
IP Whitelist Authentication
IP whitelisting allows specific IP addresses to access the API without authentication. This is useful for trusted internal systems on private networks.
Use Cases:
- Internal provisioning servers
- Network monitoring systems on management VLANs
- Ansible playbooks running on controlled infrastructure
Configuring IP Whitelist:
Add trusted IP addresses to crm_config.yaml:
ip_whitelist:
- 192.168.1.100
- 10.0.0.0/24
- 172.16.50.10
Security Considerations:
- Only use IP whitelisting on private, secured networks
- Never whitelist public IP addresses
- Use the most specific IP ranges possible
- Document why each IP is whitelisted
- Regularly audit whitelisted IPs
Example API Calls with Python
Here is an example of how to log in and retrieve a list of customers using JWT token authentication:
import requests
crm_url = 'https://yourcrm.com'
session = requests.Session()
print("Provisioning data to server: " + str(crm_url))
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
# Get Auth Token
response = session.post(crm_url + '/crm/auth/login', json={
"email": "youruser@yourdomain.com",
"password": "yourpassword"
}, headers=headers)
print(response.status_code)
print(response.json())
assert response.status_code == 200
headers['Authorization'] = 'Bearer ' + response.json()['token']
print("Authenticated to CRM successfully")
# Get Customers
response = session.get(crm_url + '/crm/customers', headers=headers)
for customer in response.json()['data']:
print(customer)