Customer Care
User Impersonation for Support and Troubleshooting
Impersonation allows authorized staff to temporarily log in as another user to troubleshoot issues, verify configurations, or see exactly what the user experiences. This feature is essential for customer support but requires appropriate permissions and is fully audited.
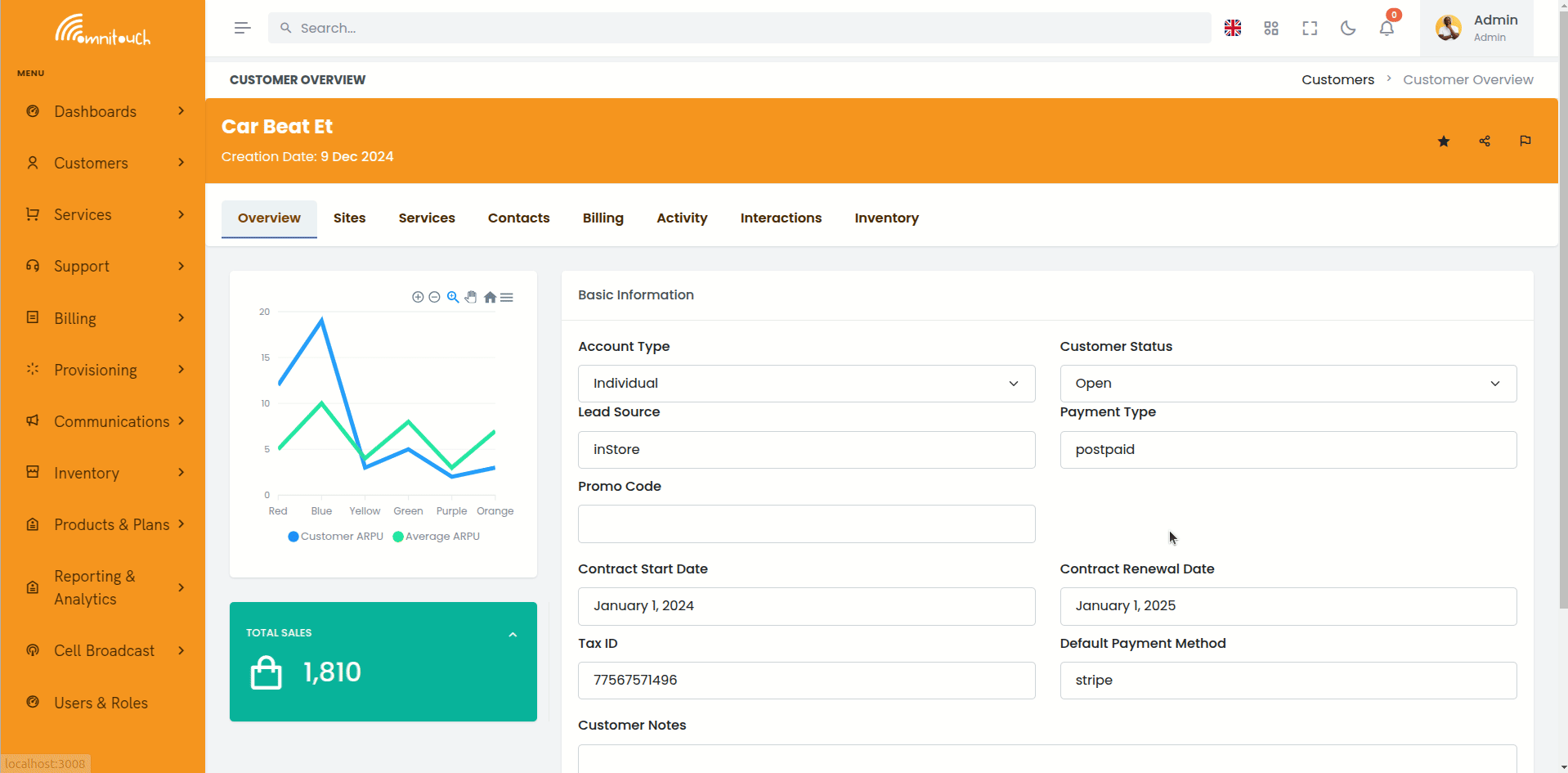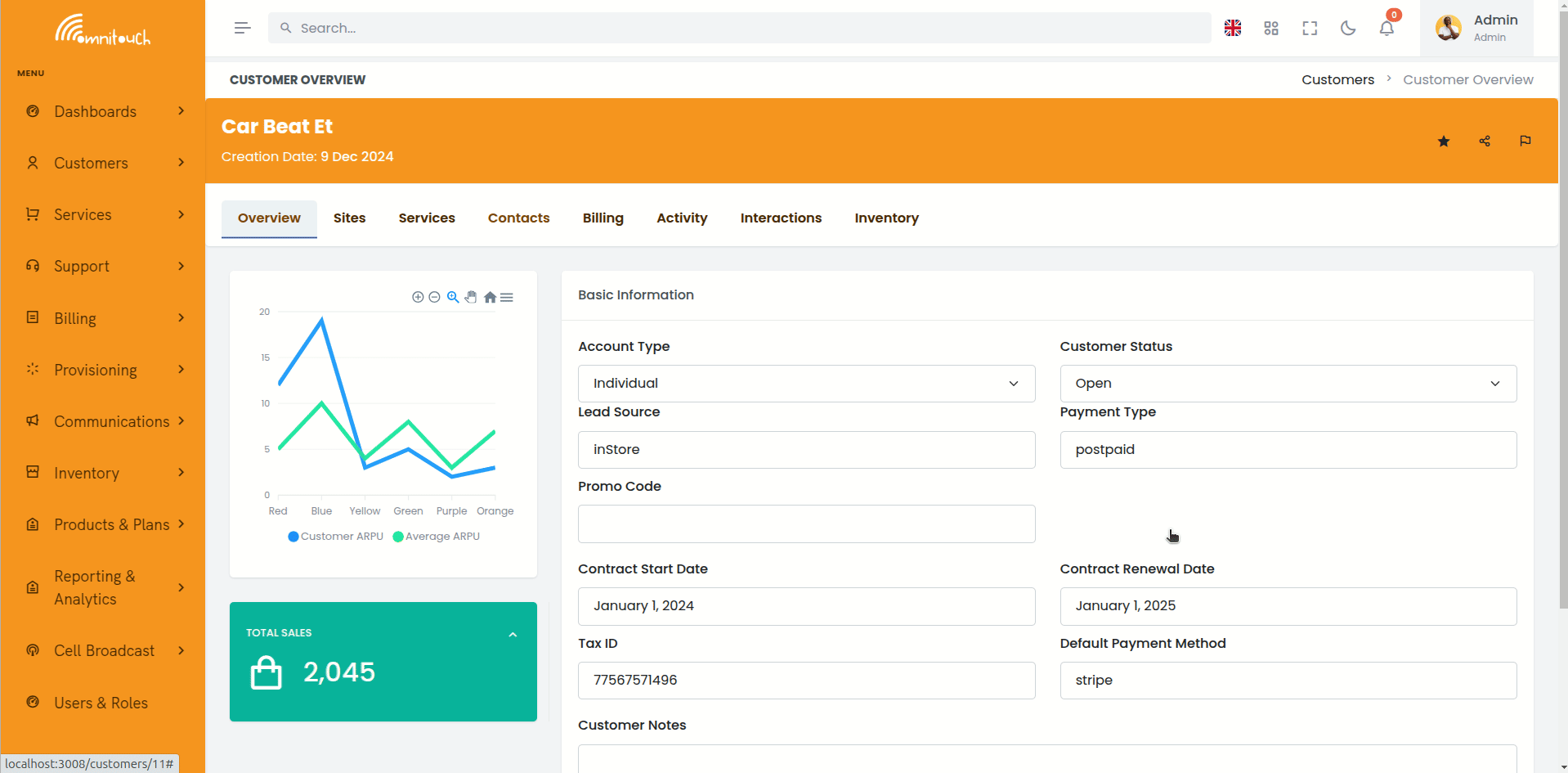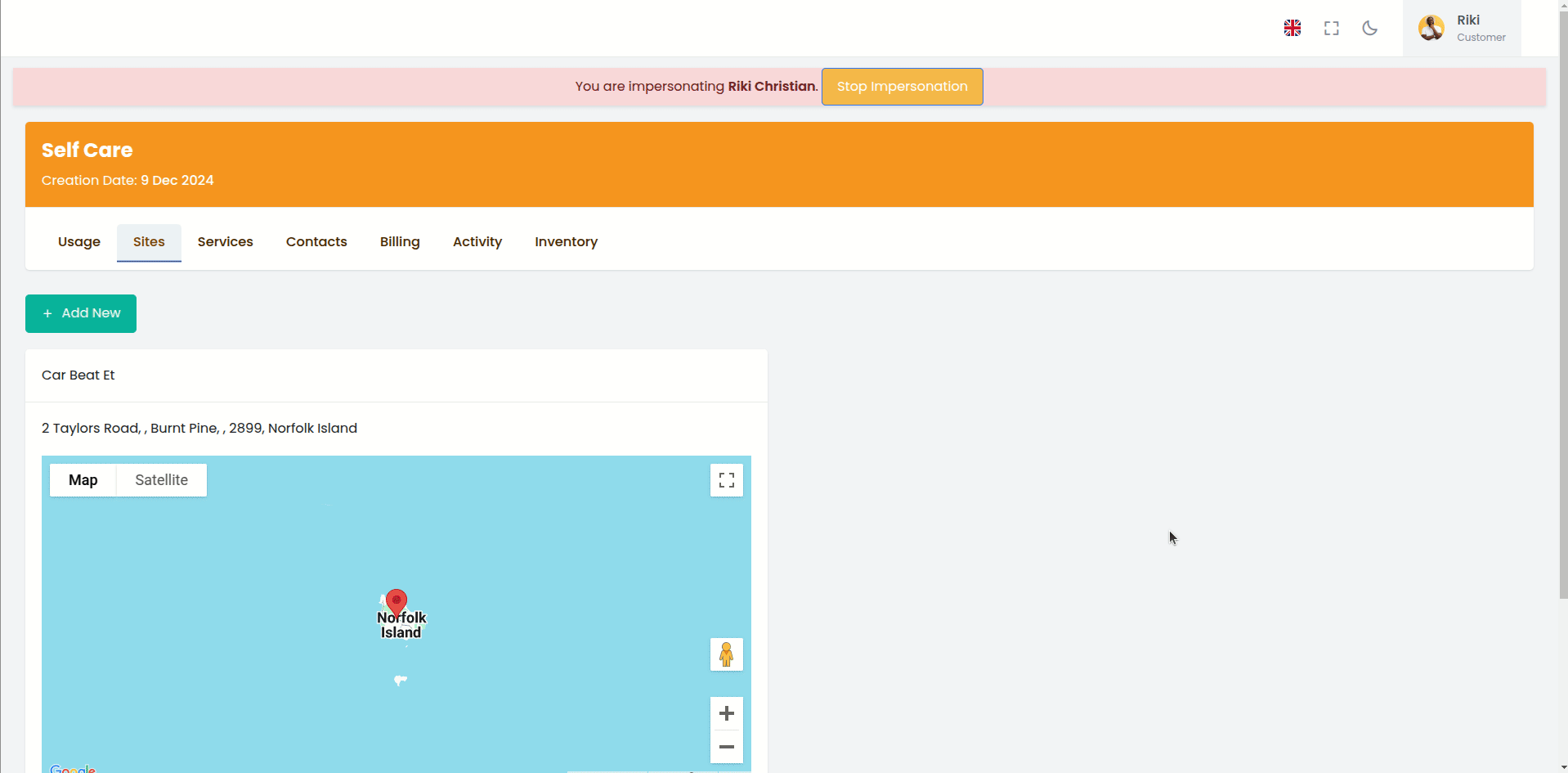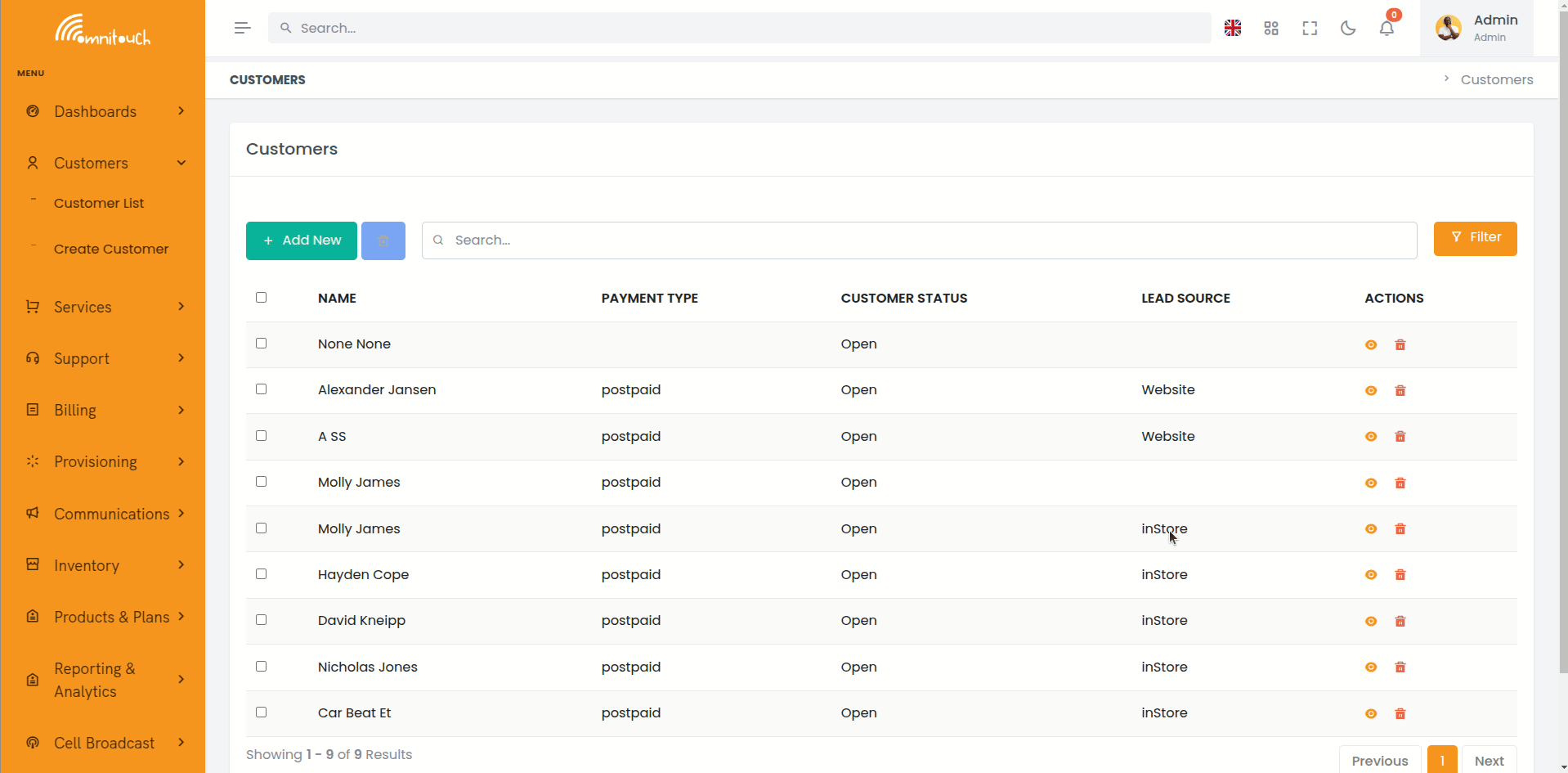
When impersonating a customer, staff access the Self-Care Portal exactly as the customer sees it, allowing for accurate troubleshooting and support.
See also: RBAC for permission configuration, Customers for customer management, Self-Care Portal for customer portal features.
Purpose
User impersonation provides:
- Troubleshooting --- See exactly what the customer sees to diagnose issues
- Verification --- Confirm service configurations and permissions work correctly
- Training --- Demonstrate features from the customer's perspective
- Support --- Help customers navigate the system without requiring screen sharing
- Audit Trail --- All impersonation sessions are logged for security and compliance
Required Permissions
To impersonate users, you must have one of the following permissions:
can_impersonate--- Dedicated impersonation permission for support staffadmin--- Full administrative access (includes impersonation rights)
Users without these permissions cannot access the impersonation feature.
How to Impersonate a User
Via Web UI:
- Navigate to Customer --- Find the customer in the CRM
- Select Contacts --- View the customer's contact list
- Click "Login as User" --- Button appears next to each contact that has a user account
- Confirm Impersonation --- System may prompt for confirmation
- Session Starts --- You are now logged in as that user
Via API:
Start impersonation session:
Endpoint: POST /auth/impersonate
Required Permission: can_impersonate or admin
Request:
{
"user_id": 42
}
Response:
{
"success": true,
"impersonating_user_id": 1,
"target_user_id": 42,
"impersonation_start": "2025-01-04T15:30:00Z",
"access_token": "new_token_for_impersonated_user",
"refresh_token": "new_refresh_token"
}
The returned tokens are for the impersonated user's session.
What Happens During Impersonation
When you impersonate a user:
- Full Context --- You see the system exactly as the target user
sees it:
- Their dashboard and navigation
- Their customer data (if customer user)
- Their permissions and access controls
- Their services, invoices, and usage
- Session Tracking --- The system tracks both identities:
impersonating_user_id--- Your real user IDtarget_user_id--- The user you're impersonatingimpersonation_start--- When impersonation began
- Indicator --- The UI displays a banner showing you are
impersonating someone:
- "You are currently logged in as [Username]"
- "Click here to stop impersonation"
- Audit Logging --- All actions are logged with both user IDs:
- Actions appear as performed by the target user
- Audit logs record who was actually performing them (impersonating user)
- Complete audit trail maintained in
ImpersonationLogtable
Stopping Impersonation
Via Web UI:
- Click Banner --- Click the impersonation banner at the top of the page
- Or Navigate --- Go to user menu and select "Stop Impersonation"
- Confirmation --- Session ends and you return to your own account
Via API:
Endpoint: POST /auth/stop_impersonation
Request: No body required (authenticated request)
Response:
{
"success": true,
"impersonation_end": "2025-01-04T15:45:00Z",
"duration_seconds": 900,
"access_token": "your_original_token",
"refresh_token": "your_original_refresh_token"
}
Your original session is restored.
Impersonation Audit Logging
All impersonation sessions are logged in the ImpersonationLog table
with:
- impersonating_user_id --- Staff member who performed impersonation
- target_user_id --- Customer or user who was impersonated
- impersonation_start --- Start timestamp
- impersonation_end --- End timestamp (when session was stopped)
- impersonation_duration --- Duration in seconds
This provides complete accountability for all impersonation sessions and allows:
- Security audits --- Review who impersonated whom and when
- Compliance reporting --- Demonstrate proper use of elevated access
- Investigation --- Track actions during impersonation sessions
- Monitoring --- Identify unusual impersonation patterns
Viewing Impersonation Logs:
Administrators can query impersonation logs via API:
GET /auth/impersonation_logs?user_id={user_id}&start_date={date}&end_date={date}
Filter by:
- Impersonating user (who performed the impersonation)
- Target user (who was impersonated)
- Date range
- Duration
Best Practices
- Minimize Duration --- Impersonate only as long as needed to resolve the issue
- Document Purpose --- Note why impersonation was needed in customer activity log
- Inform Customers --- Let customers know you may need to view their account (privacy policy)
- Verify Identity --- Confirm user identity before impersonating via their account
- Review Logs --- Regularly audit impersonation logs for unusual patterns
- Limit Permissions --- Only grant
can_impersonateto support staff who need it - Training --- Ensure staff understand the responsibility and audit implications
Security Considerations
- Full Access --- Impersonation grants complete access to the target user's account
- No Password Required --- Impersonation bypasses authentication (permission-based only)
- Logged Actions --- All actions during impersonation are attributed to target user in application logs (but audit logs show real actor)
- Session Isolation --- Impersonation creates a new session; doesn't affect target user's active sessions
- Time Limits --- Impersonation sessions should be time-limited (configurable)
- MFA Bypass --- Impersonation bypasses 2FA requirements (uses impersonator's authentication)
Restrictions
- Cannot Impersonate Admins --- Depending on configuration, may not be able to impersonate other administrators
- Same Permissions --- You get target user's permissions, not union of both users' permissions
- Session Limits --- Only one impersonation session per staff member at a time
- Audit Requirements --- Cannot disable or hide impersonation logging
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue: "Login as User" button doesn't appear
- Solution: Verify you have
can_impersonateoradminpermission - Solution: Confirm the contact has a linked user account
Issue: Impersonation fails with permission error
- Solution: Check if target user is an administrator (may be restricted)
- Solution: Verify your impersonation permission is active
Issue: Cannot stop impersonation
- Solution: Use API endpoint to stop impersonation:
POST /auth/stop_impersonation - Solution: Clear browser cookies and log in again with your credentials
Issue: Actions not logging correctly
- Solution: Verify impersonation session is active (check banner)
- Solution: Review audit logs - actions are logged with both user IDs