Customers, Contacts, Sites & Services
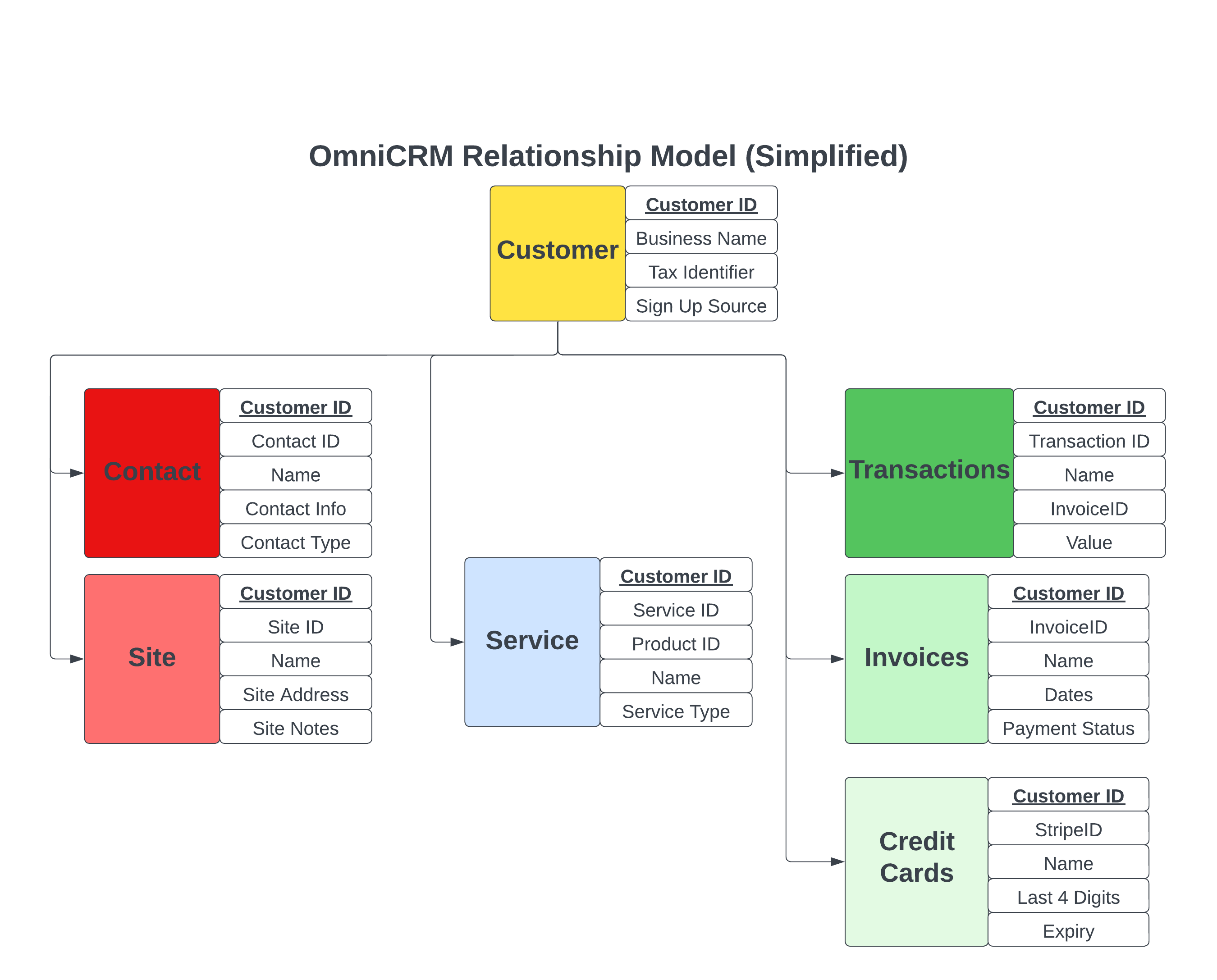
We have a simple model of a Customer under this Customer, can have multiple Contacts and multiple Sites, Services, etc.
A Customer is a company or individual who has a relationship with us, to who we send an invoice / bill.
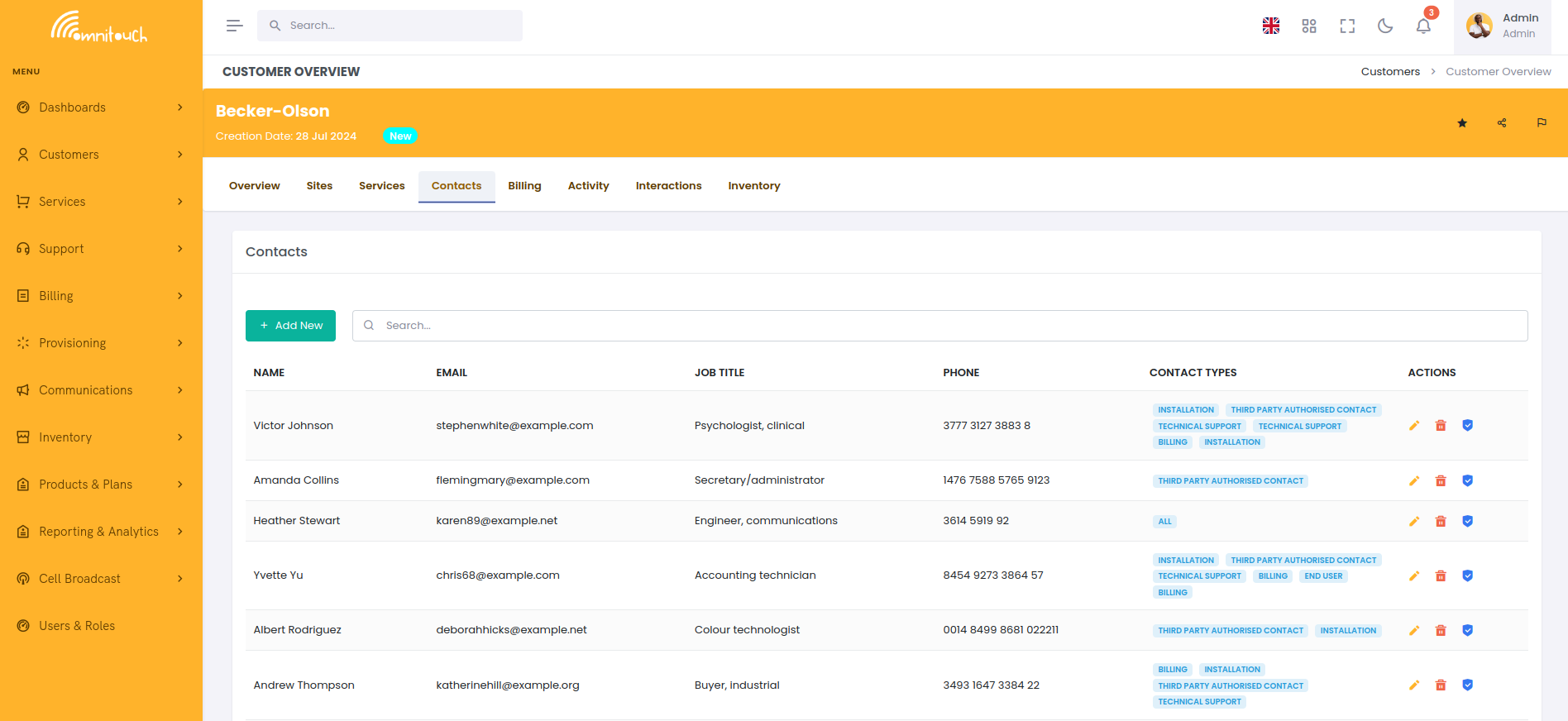
A Contact is a person who works with the customer, for an individual, it's probably the same as the customer themselves, a single person, but we might have family members or other contacts, and each contact has a type, for example a billing contact, a technical contact, etc, which influences how we handle the contact.
A Site is a physical location where we deliver services, it could be a home, office, or other location. This allows us to have multiple sites for a single customer, for example, a customer with multiple offices, and know which services are associated with which site.
A Service is something we bill a customer for, it could be a home internet service, mobile service, or even abstract services like leasing a subnet or providing metered electricity to a rack. Each service is linked to a customer and a site, and can have multiple charges associated with it.
Customers also have an Activity Log , which is a record of all the changes made, Tags , Attributes for storing custom metadata, Inventory Items and financial information like Transactions , Invoices & Payment Methods .
Once we've created a customer we can then add a service to that customer, which is the thing we bill them for.
For information on creating a customer, see Create a Customer .
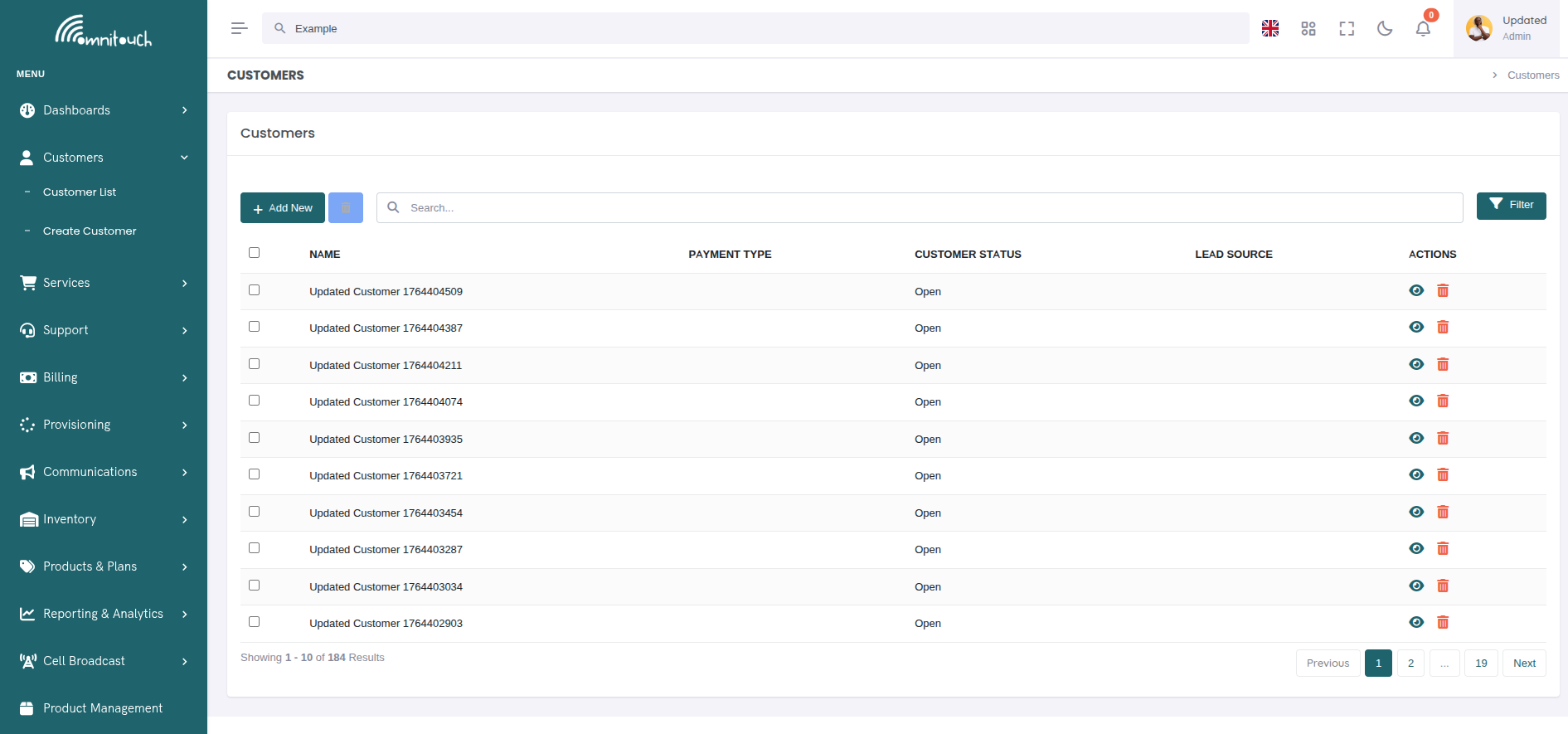
Customer List
The customer list provides a searchable, filterable table of all customers in the system.
 {.align-center
width="800px"}
{.align-center
width="800px"}
Features:
- Search - Filter customers by name or ID
- Bulk Actions - Select multiple customers for batch operations
- Pagination - Navigate through large customer lists
- Quick Actions - View or delete customers directly from the list
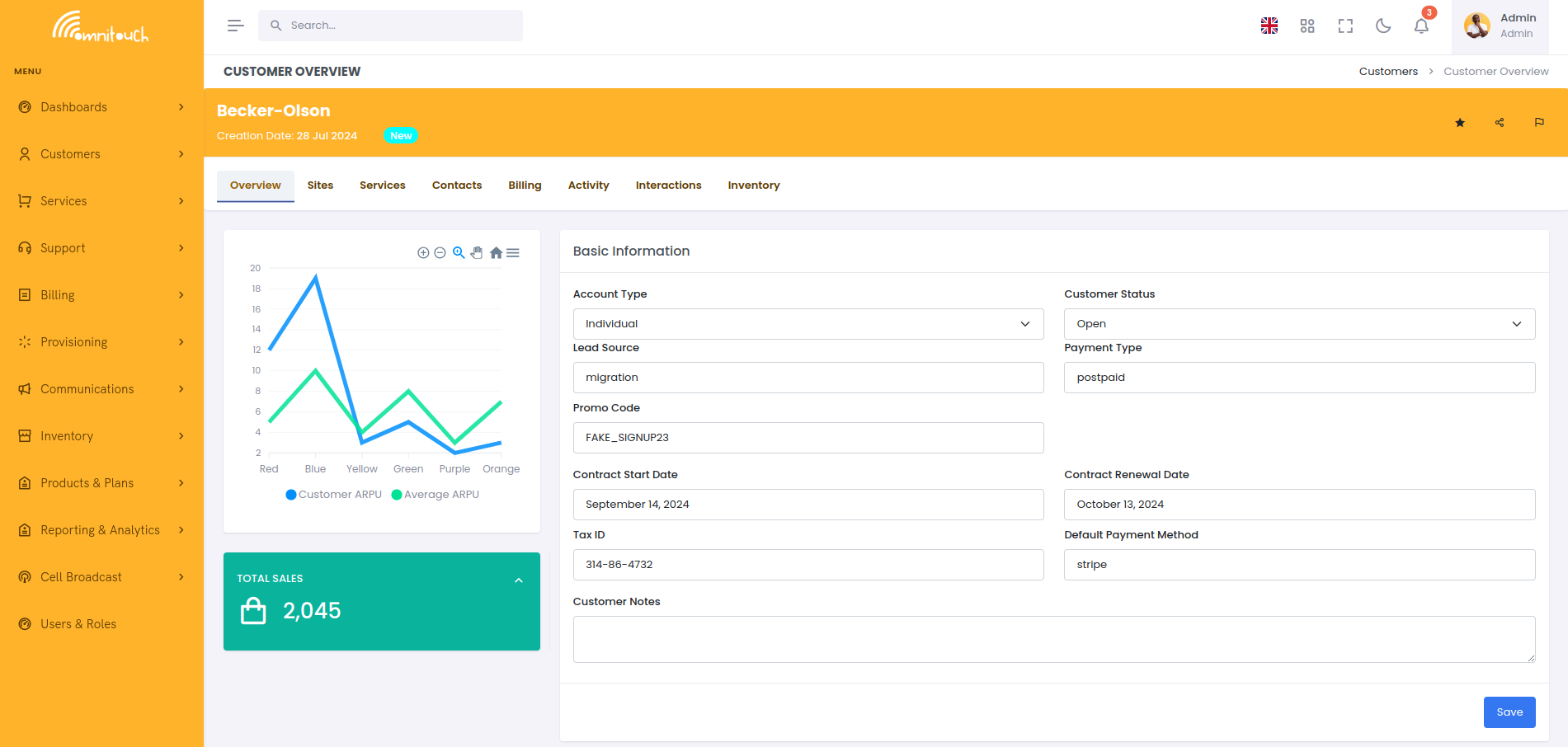
Customer - Detail
The customer object itself does not contain much information, it's just a name and a reference to the contacts and sites.
Your specific deployment may include additional fields or customizations, but the basic customer object is very simple.
On the overview page is also a graph showing the Average Revenue Per
User (ARPU) for the customer, which is
the total revenue divided by the number of services, and a comparison as
to how this customer compares to the average ARPU for all customers in
the system.
The Customer Status options are tailored based on the specific needs of your business, but typically include options like Active, Inactive, Pending, etc, with different rules in each that control the behavior of the customer in the system in that state.
Deleting a customer can only be done if the customer has no active services, unpaid invoices or uninvoiced transactions. If the customer has any of these, you will need to close the active services and ensure the payments are made before you can delete the customer, which in turn will archive the customer and all associated data, which can later be restored if needed.
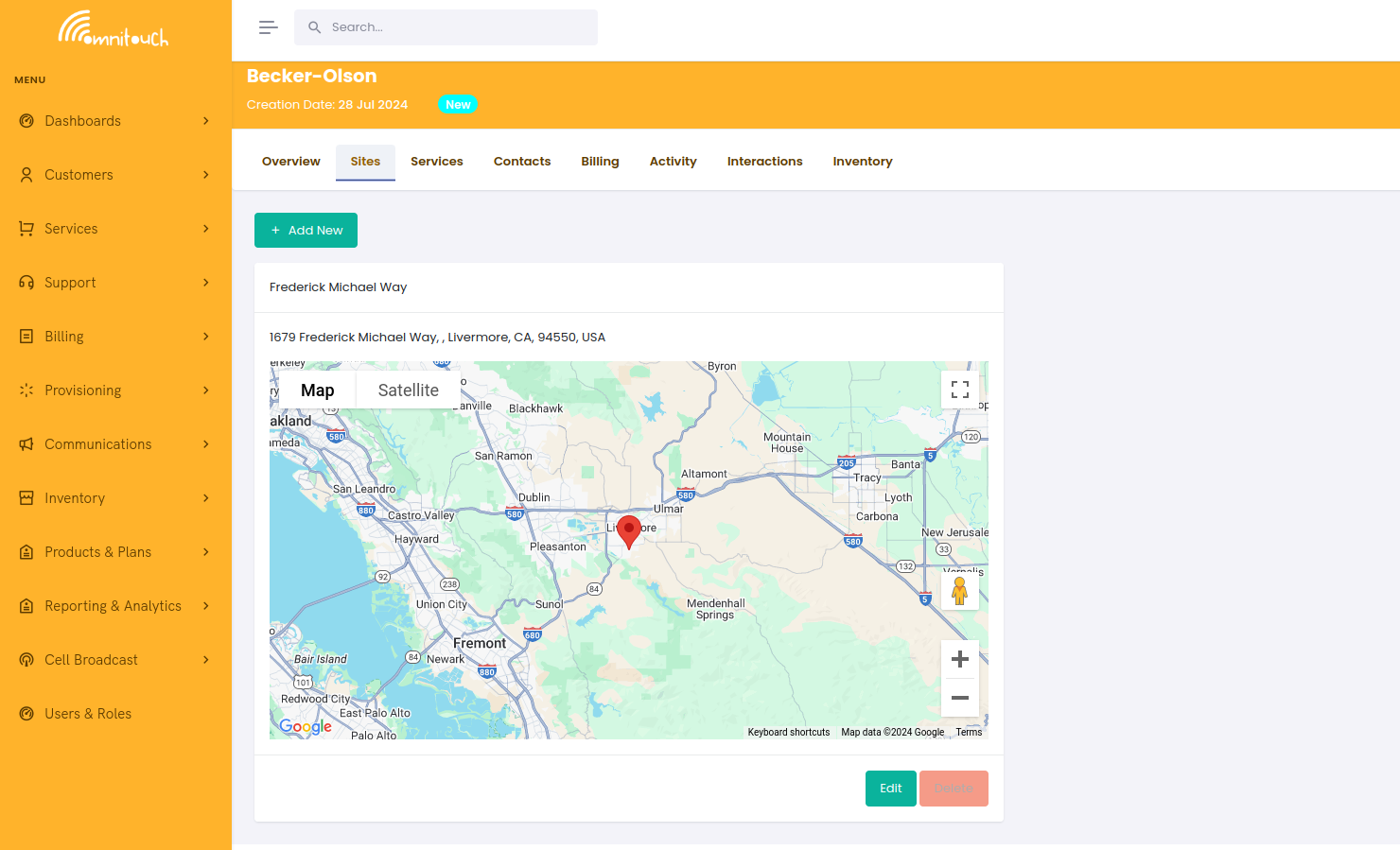
Site - Detail
Sites are physical locations where services are delivered, and can have multiple services associated with them.
They are predominantly used for business customers, where a single customer might have multiple sites, for example, a customer with multiple offices.
Having multiple sites allows us to track which services are associated with which site, for example if a customer orders a new service for a new office, we need to make sure that we deliver the correct service to the correct location. This allows us to track services by site and to bill them separately if needed.
Google Maps Integration and Geocoding
Each site is integrated with Google Maps to ensure accurate address data and geolocation. The UI automatically geocodes addresses and generates location data.
How Address Geocoding Works:
When adding or editing a site, the interface provides two methods for setting location:
- Address Search (Recommended)
- Use the search bar at the top of the form
- Type an address and Google Maps Autocomplete suggests matches
- Select the correct address from the dropdown
- The system automatically populates:
- Site Name - Place name from Google Maps
- Address Line 1 - Street number and name
- Address Line 2 - Subpremise (unit/suite number)
- City - Locality
- State/Region - Administrative area
- Post Code - Postal code
- Country - Country name
- Latitude & Longitude - Precise coordinates
- Plus Code - 11-character Open Location Code (e.g.,
8C3MFJV8+2F) - Google Maps Place ID - Unique place identifier
- Draggable Map Marker (Manual)
- Drag the pin on the map to the exact location
- System performs reverse geocoding to get address from coordinates
- Same fields auto-populate based on pin location
- Useful for rural areas or when address is imprecise
Plus Code Generation:
Plus Codes are automatically generated from latitude/longitude using the Open Location Code library. A Plus Code is a short code (11 characters) that represents a precise location anywhere in the world.
Example:
Auto-populated fields: ✓ Site Name: "123 Main Street" ✓ Address Line 1: "123 Main Street" ✓ City: "London" ✓ State: "Greater London" ✓ Country: "United Kingdom" ✓ Post Code: "SW1A 1AA" ✓ Latitude: 51.5074 ✓ Longitude: -0.1278 ✓ Plus Code: "9C3XGPHC+3Q" ✓ Google Place ID: "ChIJdd4hrwug2EcRmSrV3Vo6llI"
Validation Requirements:
Before saving a site, the system validates:
- Latitude & Longitude must be set (either via search or dragging marker)
- Country must be populated (defaults to
REACT_APP_DEFAULT_COUNTRYif not set) - Plus Code must be 12 characters (11 + 1 for padding)
If validation fails, you'll see an error:
Visual Feedback:
The interface shows real-time feedback:
or
How Location Data is Used
The geocoded location data (latitude, longitude, Plus Code) is used throughout OmniCRM for:
1. Service Delivery and Installation
- Field Technicians - Access Plus Code to navigate to exact site location
- Installation Scheduling - Assign techs based on geographic proximity
- Equipment Deployment - Ensure correct equipment delivered to correct site
2. Outage Notifications
- Geofenced Alerts - If network outage in specific area, query sites by lat/long radius
- Targeted Communications - Send outage notifications only to affected customers via Mailjet
- Status Pages - Display outage map with affected sites
Example:
Query: SELECT * FROM Customer_Site
: WHERE distance(latitude, longitude, 51.5074, -0.1278) < 5
Result: 47 affected sites Action: Send outage notification to 47 customers
3. Reporting and Analytics
- Geographic Revenue - Revenue by city, state, region
- Service Density Maps - Heatmap of service locations
- Expansion Planning - Identify underserved areas
4. Multi-Site Business Customers
- Site Management - Track which services at which locations
- Separate Billing - Invoice by site if required
- Service Assignment - Link services to specific sites during provisioning
Rural and Remote Sites
For customers in rural areas where street addresses may not exist or be inaccurate:
- Use Map Drag
- Zoom into the approximate area
- Drag the pin to the exact property/building
- System generates Plus Code for that precise location
- Plus Code Sharing
- Share Plus Code with customer (e.g.,
8C3MFJV8+2F) - Customer can enter this in Google Maps to see exact location
- Field techs use Plus Code for navigation
- Share Plus Code with customer (e.g.,
- Address Notes
- Use "Address Note" field for additional directions
- Example: "Turn left at red barn, 500m past cattle grid"
- Notes visible to installation teams
::: tip ::: title Tip :::
You can drag the pin on the map to the correct location if the address is not accurate. The system will reverse-geocode the location and populate all address fields automatically. :::
Contact - Detail
The Contacts are people associated with the customer. They can be billing contacts, technical contacts, or other types, and each contact has a type that influences how we handle the contact.
We can have multiple contacts for a single customer, for example, a customer with multiple billing contacts, or a customer with multiple technical contacts.
A good example would be a company with a managed service provider, who handles the technical side of things, and a separate billing contact who handles the financial side of things, or a family where each member has their own contact but not all are authorized to make changes.
Likewise we may only want to send outage notifications to the technical contact, or only send invoices to the billing contact, and the contact type allows us to control this.
The exact logic of how contact types are used is up to your business, but the basic idea is that each contact has a type that influences how we handle them, and that each person who is associated with the customer is a contact.
Contacts are synced with the Mailjet integration, allowing us to send targeted email campaigns based on the contact type, location, monthly spend, or purchased services, and to manage all email templates used for transactional communications.